
What Is a Customer Journey Map? A Detailed Guide
You will have conducted the initial UX deliverables. After conducting user research and creating user personas, customer journey maps comes. These are a crucial part of the UX design. With the help of customer journey maps, you can properly visualize the user experience and interaction with the design. It is a kind of deep-level analysis of the customers.
Therefore, we will help you understand the importance and process of customer journey maps in this article.
After reading this article, you will learn:
- What is a customer journey map?
- Benefits of creating a customer journey map
- Essential elements of a customer journey map
- How to create and fill a journey map?
- Difference between customer journey maps and some UI design deliverables
What is a customer journey map?
Organizations and businesses need to have strong communication with the audience. Quality service or product can keep this connection. Therefore, you will need to create appealing and user-oriented designs.
In this regard, customer journey maps will help you understand the audience’s needs.
A customer journey map is a customer’s experience with your business’s product or service while accomplishing a certain task. It implies the whole process from the initial interaction to the final purchase. A customer journey map will depict the whole user interaction visually.
Hence, you will get extensive visualization of the user experience. Ultimately, your product or service design will improve.
A customer journey map (also referred to as a user journey map) includes different aspects of the potential customer. It includes the research phase, user problems, goals, product interaction, and final purchase. It possesses all the core aspects of a design process– storytelling, user experience, user interaction, and visualization. These features make it effective for the design success. Therefore, it is one of the most commonly used design tools.
Example of a customer journey map:
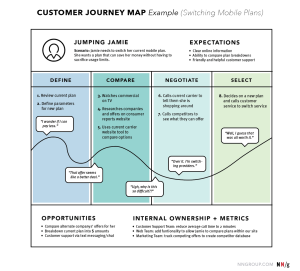
Image credit: N N Group
Benefits of creating customer journey maps
- Build empathy:
Building empathy is one of the most important benefits of a customer journey map. Empathy is all about user identification. After creating a perfect customer journey map, you will be able to understand user emotions, feelings, motivations, and experiences.
All information about the user is presented in the form of storytelling. Hence, it displays the user portfolio convincingly.
- Define pain points:
You can’t sell customers your product if you don’t know their pain points. Your customer journey map should address customer’s pain points. In this way, you can sell them solutions.
An effective customer journey map will help you clearly define user frustrations and pain points. Therefore, you must create a customer journey map.
- Improve design process and results:
The ultimate result of an effective customer journey map is an improved design process. This design process will help you achieve high conversions and sales. Therefore, a customer journey map is a must for your design strategy.

Image credit: UX Design
Format of a customer journey map
A customer journey map hasn’t a one-size-fits-all formula. Its format varies, respecting different business and audience requirements.
Customer journey maps come in different sizes, formats, designs, and styles. You can select a perfect journey map format according to your requirements.
However, a customer journey map follows some essential elements. These are common in all types of customer journey maps.
Top area:
At the top area, details of the specific user, scenario, expectations, and goals are given.
Main area:
The main area of the customer journey map includes different phases of user tasks, including user actions, thoughts, and emotions. It is situated in the middle.
Lower area:
At the bottom, details of the insights, internal ownership, insights, and conclusions are given.
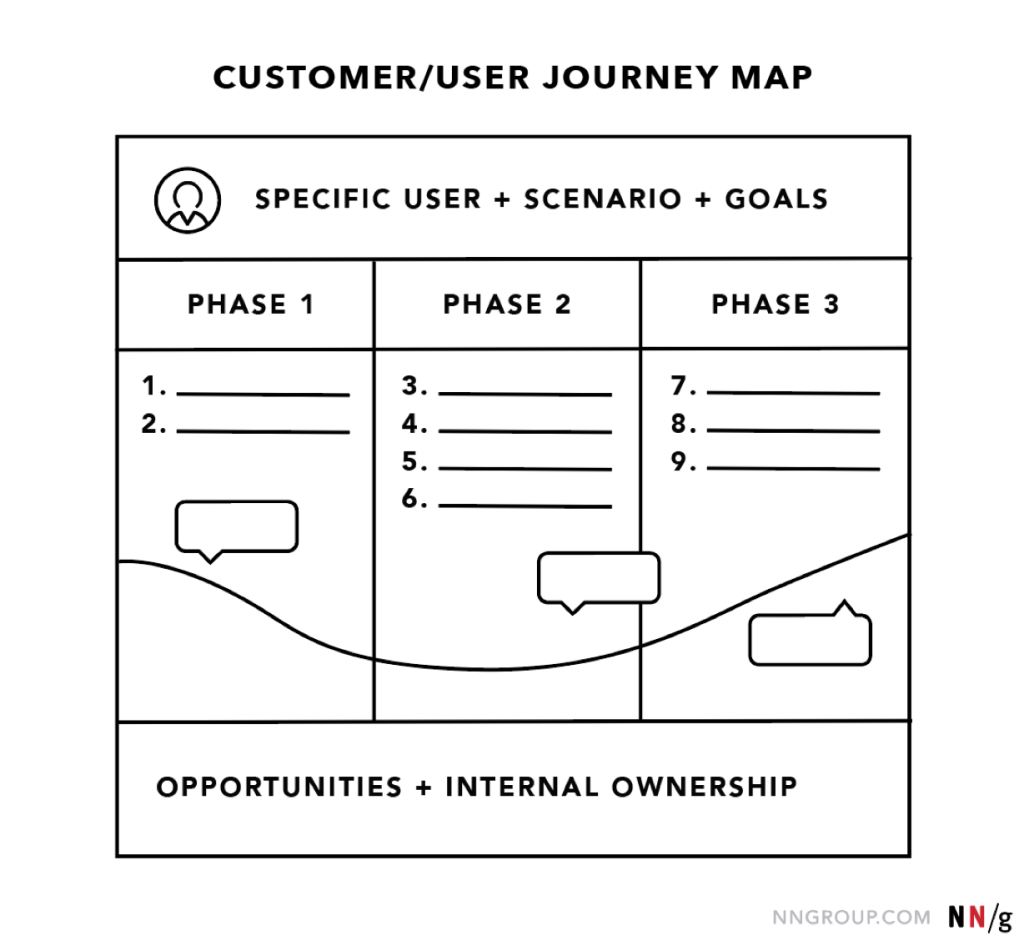
Image credit: N N Group
Essential Elements of a journey map:
A customer journey map revolves around 5 main components. These are crucial for a perfect journey map.
- Actor:
Actor is the main character of the persona. It represents your potential customer. You can derive the details of your potential customer or user from the existing user persona.
It is always focused on a single idea. Hence, you can get precise results.
- Scenario:
A scenario is the central element of a customer journey map. It focuses on user needs and expectations. This way, you can generate a user-oriented scenario. Every customer journey map has a specific scenario. Multiple scenarios in a single journey map create confusion.
You can use real scenarios for the existing products or services. These will be based on previous user experience. However, you can also set up idealistic scenarios based on analytics. They will help you formulate a clear design strategy with user context. Hence, user journey maps are the best way to build user scenarios.
- Phases of journey map:
Phases depict the gradual steps of user interaction. These discuss different stages of user behaviors, emotions, thoughts, and experiences. Every customer journey map has its own customized phases. These journey phases vary from scenario to scenario.
- Actions, emotions, and thoughts:
Customer journey maps display user actions, emotions, and thoughts at different levels. It shows their needs, behaviors, activities, frustrations, motivations, and mindsets.
- Opportunities:
Opportunities are the desired results. They produce recommendations, along with metrics and ownership. These opportunities help answer core questions regarding product design and user experience.
How to create and fill a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is backed by user research, persona, and competitive analysis. It requires a realistic approach to deduce authentic insights. Therefore, your designers must follow all the essential steps to create a perfect journey map. Below, we have discussed the main steps of creating a customer or user journey map.
- Group setting:
First, you will need to set up designers and product managers teams. You can arrange small teams of 3-5 members each. The number of teams will depend on the business and audience requirements. You can decide the number of teams based on complex design processes and large businesses. One thing is common– consensus. Teams should have strong communication to build a common strategy.

Image credit: UX design
- Formulate the basics:
Business goals and user research build the foundation of a customer journey map. In the beginning, you will need to discuss the business goals and user requirements with the teams. In this way, you will get a strong foundation.
Try to find the answers to these questions.
- What are your business goals and requirements?
- Who is your audience?
- What are their goals and expectations?
- What are the initial process requirements?
- What kind of user personas will be used?
- Initial process:
The initial process includes the analysis of the following UX deliverables:
- UX research
- User interviews
- User surveys
- User personas
- Competitive analysis
After that, your team can draft the initial design of the customer journey map. They may use a pencil and paper. Sticky notes are beneficial in this regard. They can also use an excel sheet.
However, they can also use a digital customer journey map template. You can find quality journey map templates on Canva, Adobe XD, and UXPressia.
Once designers have selected the template, they will need to add the main sectors of a customer journey map.
- Actor:
A perfect journey map focuses on a single character. Your user persona will provide that character. The actor’s role needs to be clear and specific. In this way, you can easily target the results.
For example:
A University may have two types of users. It may focus on a student or faculty member. So, it will have to choose a single user at one time. In this way, the results will be clear and compelling.
- Scenario and expectations:
Scenario building comes after identifying the actor. The existing scenario will work for the renovation of old products. However, you will need to use an estimated scenario for a new product design. The scenario needs to be specific and targeted toward the customer. Hence, it will help define the user experience.
- Journey map phases:
Different high-quality phases make the essential part of a user journey map. They talk about user actions, thoughts, emotions, and motivations.
Your designers need to identify the first, middle, and last phases. Thus they can visualize the whole user interaction.
Furthermore, phases depend upon scenarios. Different scenarios contribute to different journey phases. In this regard, journey phases will be different for different businesses. However, the format will be the same.
For example:
For an educational scenario, the stages may be observation, research, analysis, education, and deduction. In comparison, stages may be research, product evaluation, purchase, adoption, retention, and review.
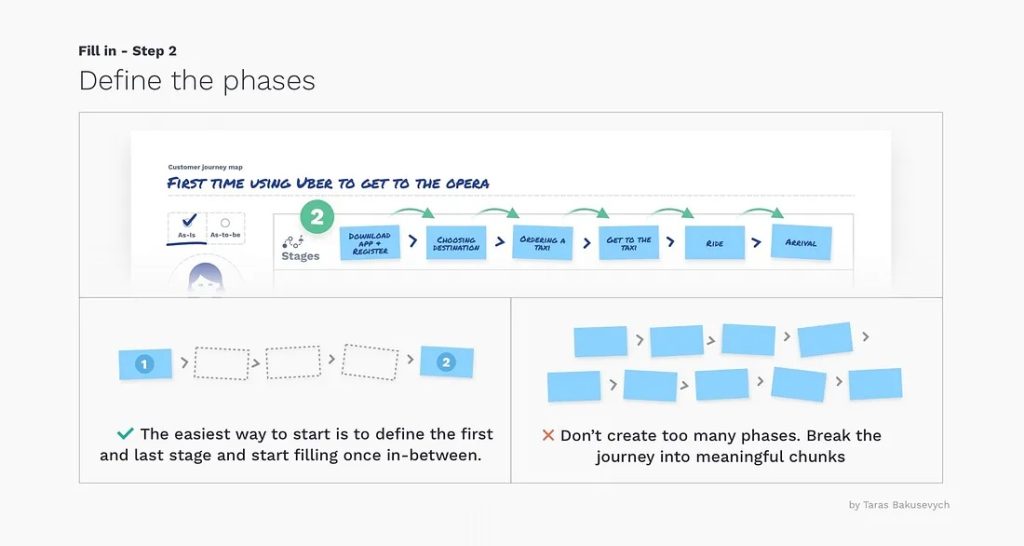
Image credit: UX Design
- Actions, emotions, and thoughts:
Actions, emotions, and thoughts are part of the whole journey map. They display a complete view of the user experience.
Actions: Actions are user behaviors during the journey process. They include the complete set of tasks accompanied by the design process.
Emotions: Emotions represent user frustrations, pain points, and feelings in a single journey line.
Thoughts: They consist of users’ mindsets, motivations, and ideas. Users depict them in the journey phases.
- Opportunities:
Opportunities, ownership, and metrics are the insights a design team derives from mapping. They highlight user experience optimization. Simply put, opportunities will help you deduce the potential advantages and strategies for an effective design process.
Designers will analyze the opportunities based on user interaction with the product. In this regard, a customer journey map will visually depict the user interaction. Finally, they will add insights to the journey map. Make sure they perform this step rightly. Your whole design process will depend on the actual insights.
Mainly, opportunities will help you answer these questions:
- What is needed to be changed?
- How can you use the user knowledge?
- How should you measure improvements?
- Touchpoints:
Touchpoints are digital or physical interactions with services, people, or other tools. Simply put, touchpoints depict the user interaction other than the primary design interaction.
They help identify opportunities and visualize user models. For effective touchpoints, designers should add only relevant data. It is not a service blueprint. Therefore, they need to keep it concise.
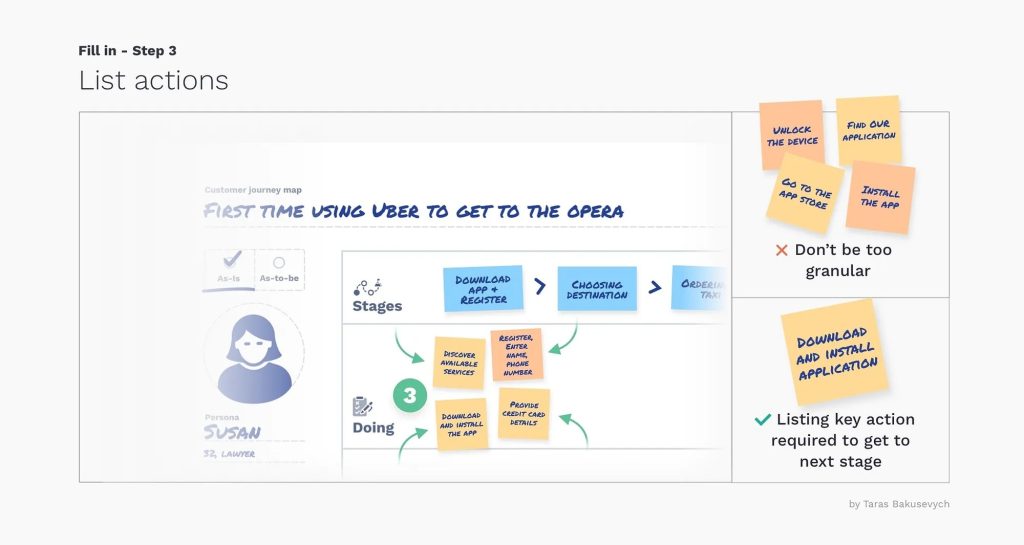
Image credit: UX Design
- Make an empathy map:
An empathy map provides beneficial user knowledge. It visualizes the user experience in a certain situation. Hence, it helps understand the users thoroughly.
- Step-by-step process:
Designers will fill the journey phases in this stage with progressive user experience.
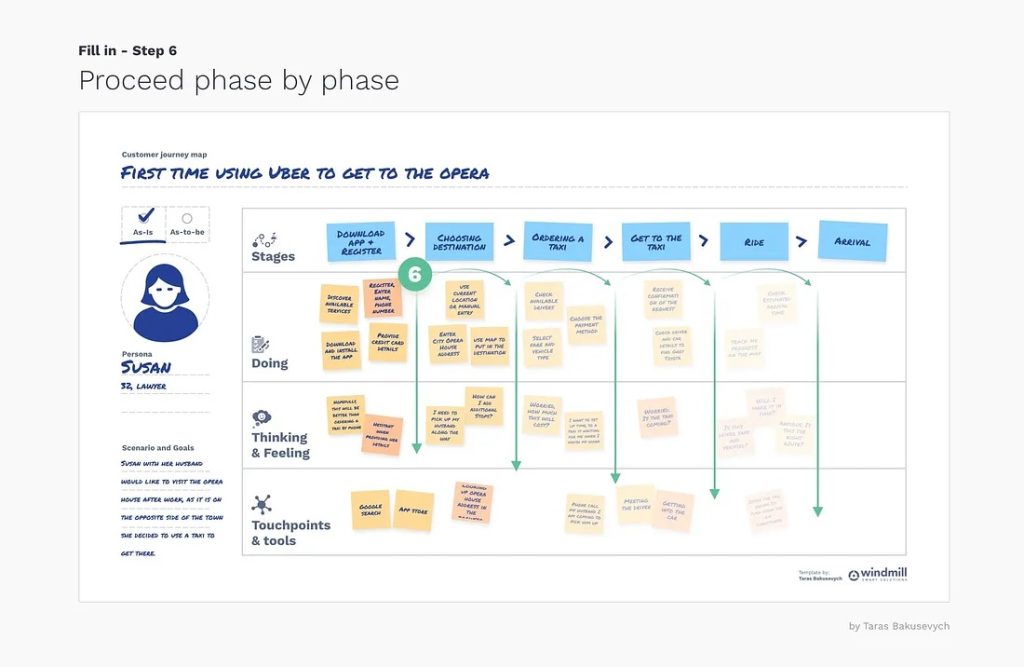
Image credit: UX Design
- Revision and iteration:
Final step includes the revision of the customer journey map. Revision helps make the best version of the customer journey map. After the revision and iteration, you will get a complete customer journey map. After the revision, share the customer journey map with the stakeholders. It will help gain beneficial feedback for the improvements.
Clear concept of customer journey maps:
People confuse journey maps with some other UX deliverables. Here is the differentiation among them.
- Difference between as-is and to-be customer journey maps:
As-is customer journey map talks about the current experience. In comparison, the to-be customer journey map discusses the future experience. You can adopt any of the journey maps according to your requirements.
- Difference between customer and user journey maps:
Difference between customer and user journey maps depends on the type of persona. It means they differ in the type of character. Simply put, a user may sometimes be a customer. In some instances, a customer represents a specific group. Hence, these two journey maps represent two different characters. However, these are generally used interchangeably.
- Difference between journey and experience maps:
A journey map introduces a specific user and scenario. It is focused on a specific product or service. However, an experience map is a broad term. It introduces the overall user experience during the design process. It identifies the broad user base with human experience.
- Difference between a journey map and service blueprint:
A journey map talks about the user perspective. It runs the actual design process. In comparison, the service blueprint tells about the business perspective. It runs at the back side of the design process. Hence, it depicts the relationships among different service elements.
- Difference between journey and user story maps:
A journey map discovers and understands an extensive perspective of user stories. However, a user story map focuses on a lower level. It visualizes the user story. A user story is a short description of a user’s goal and the benefit he will get by using the product feature.
More Articles to Read
A customer journey map is the visualization of the user experience efficiently. You will need to exercise professional strategies to create a perfect journey map.
In return, it will greatly improve the design process. Resultantly, you will develop a better user experience. This user experience will lead you to product sales and business growth.




